What Is An Electric Fuse?
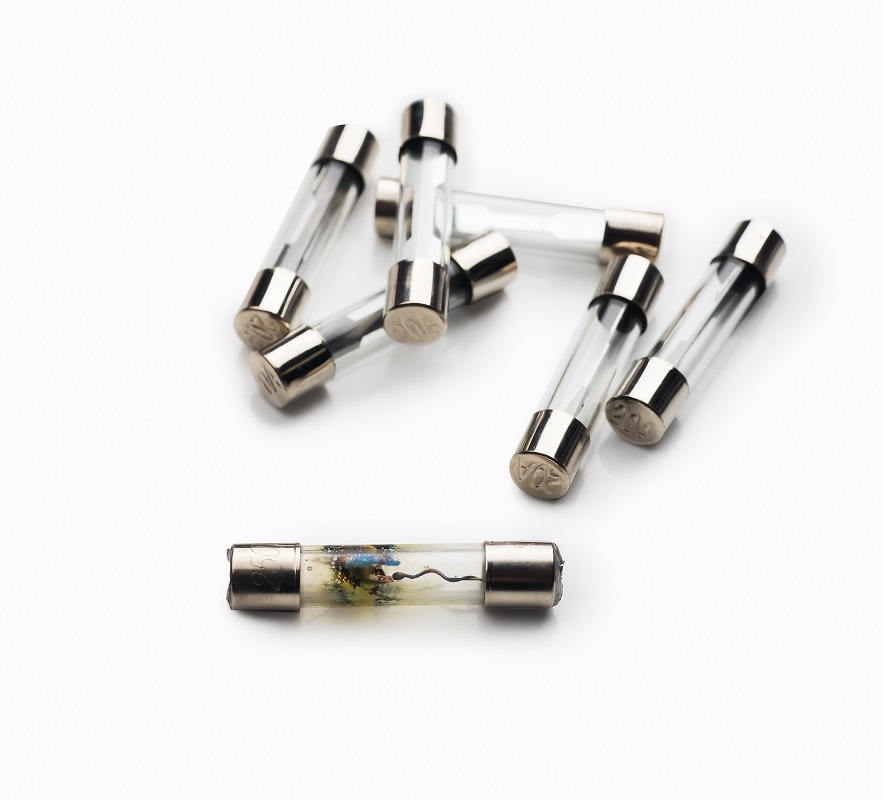
An electric fuse is a safety device use in electrical circuits to protect them from excessive current flow. Its main purpose is to prevent damage to the circuit or the connected devices by interrupting the flow of electricity when the current exceeds a certain threshold.
The basic construction of an electric fuse consists of a thin strip or wire made of a material with a low melting point, typically copper or silver. This strip is placed within a protective housing, which is connect in series with the circuit being protect. When the current passing through the fuse exceeds its rated value, the strip heats up due to the increased resistance. And eventually melts or breaks, causing an open circuit.
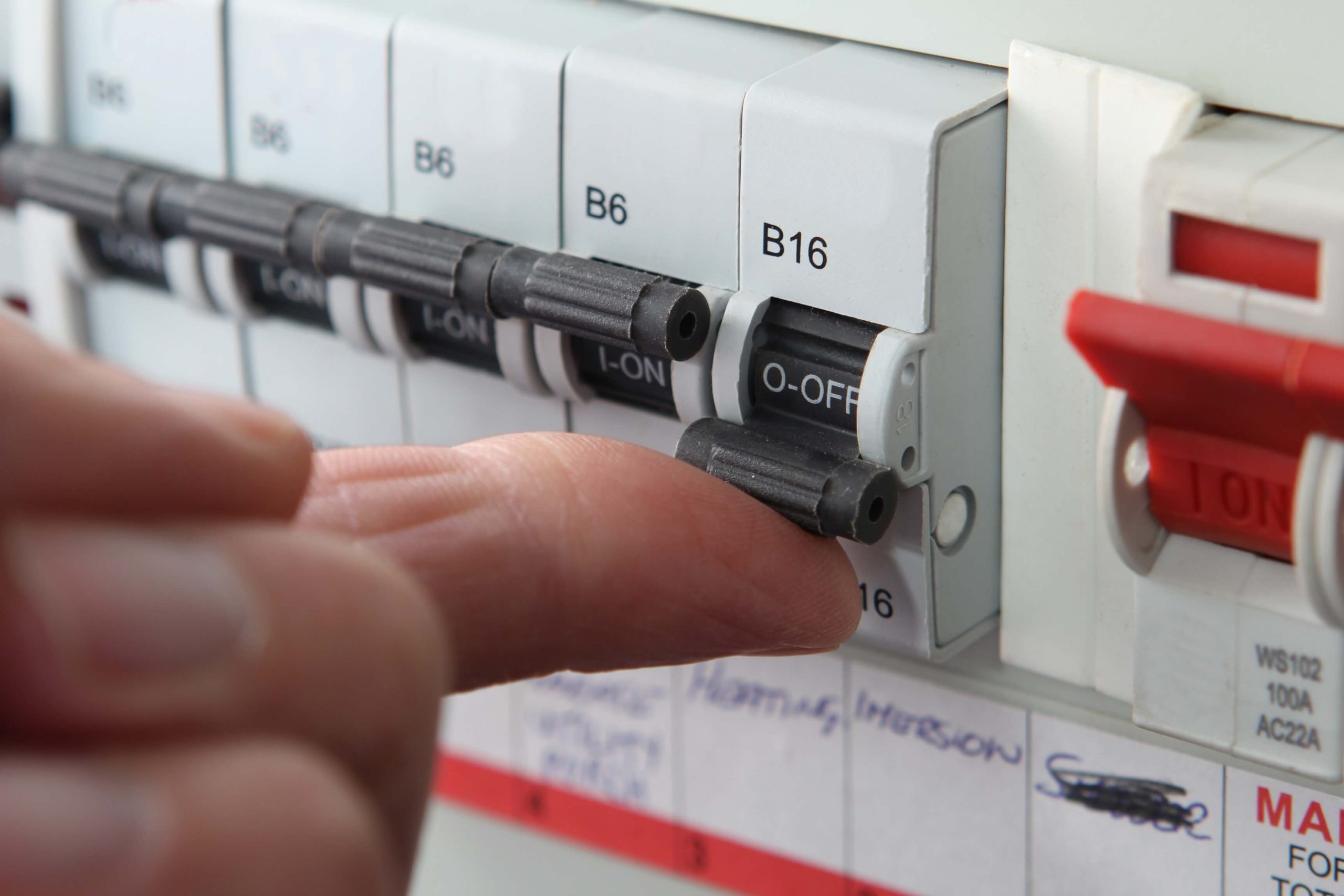
How Does An Electric Fuse Work?
According to the National Electrical Code, a fuse is consider an Overcurrent Protective Device(OCPD). A fusible portion, or element that can melt, is need for one fuse to serve effectively. This is a glass fuse body with an essence ring seal inside it; it’s appertain to as a fusing element. The fuse element heats up and melts when it absorbs further energy than it can manage. The circuit breaks, indicating that it’s complete and secure. The fuse must be replace with a new bone after this occurs.
What Differentiates a Circuit Breaker from a Fuse?
Circuit breakers and fuses are both used for electrical circuit protection. But they have some key differences in their operation and features. Here are the main differentiating factors between circuit breakers and fuses:
Resetting: One of the significant differences is that a fuse is a one-time use device that must be replace after it has melted or blown. Once a fuse breaks the circuit due to excessive current, it needs to be replace with a new fuse of the correct rating. On the other hand, a circuit breaker is a reusable device that can be manually reset after it trips. When a circuit breaker detects an overload or a fault, it interrupts the circuit. But it reset by flipping a switch or pushing a button once the issue is resolve.
Response Time: Circuit breakers generally have a faster response time compared to fuses. Circuit breakers can detect and interrupt excessive current or faults within milliseconds, whereas fuses may have a slightly slower response time.
Sensing Mechanism: Fuses operate based on the principle of a thin strip or wire melting due to heat generated by excessive current. In contrast, circuit breakers use various mechanisms to sense the current, such as thermal, magnetic, or electronic sensors.
Flexibility and Adjustability: Circuit breakers offer more flexibility and adjustability compared to fuses. With a circuit breaker, you can manually set the desired current rating or adjust the trip settings according to the specific requirements of the circuit. Fuses, on the other hand, have fixed current ratings, and you need to select the appropriate fuse with the correct rating for the circuit.
What Are The Various Fuse Types?
Your house will be safe from fires and other harm with the right fuse box. There are currently three types of fuses on the market:
- Type-S (Dismissal base) These circuits accompany a breaker and a connector that might be embed into an Edison-style attachment.
- Wires with the Type-T (Edison base) assignment are the standard for all intents and purposes each of the 120 to 125-volt homegrown circuits.
- Charger Fuses: The fuses are use in 240-volt appliance circuits and are use to control the power of the fuse box.
How Come Fuses Blow?
At the point when a high-volume flow ventures by means of a low-obstruction electrical highway, a short out is made. Electric links can be puncture by a nail or screw, permitting water to enter the info jack and bringing about a short out. Because they are a thousand times stronger than the average current. They can damage wire insulation, burn metal, start fires in arches and evaporate conductors.
When a charged hot wire meets something ground. Such as a metal pipe, power box, your palm, bare neutral wire or an outlet. A ground fault causes the electric fuse to blow. An electric overload that is also six times the typical flow of current could cause the circuit to open and the fuse to blow. At the point when there are such a large number of gadgets connect to one circuit, over-burdens normally happen.
How do I know if a fuse has been blown?
You can decide if a circuit has blown outwardly or utilizing the guide of a device known as a congruity analyzer or ohmmeter. Visual testing will enable you to determine whether the screw-in fuse pane is clear. Whether the fuse’s fusing component has been severe inside the fuse box. Because of the dissolving melding fixing, it could appear to be brown, dim, or dark.
Instrument for Testing: You can quantify opposition with instruments like ohmmeters and coherence analyzers. When inspecting a screw-in fuse, keep one test lead attached to the fuse’s end and the other to the screwed side.
Conclusion:
The electric fire can occur when electricity overflows and causes damage to your devices or even human life. As a result, putting in place a suitable device, such as a fuse or circuit breaker. In your home to protect it from electrical problems is a must. Additionally, it would be best to make that decision with the assistance of a licensed and seasoned electrician.